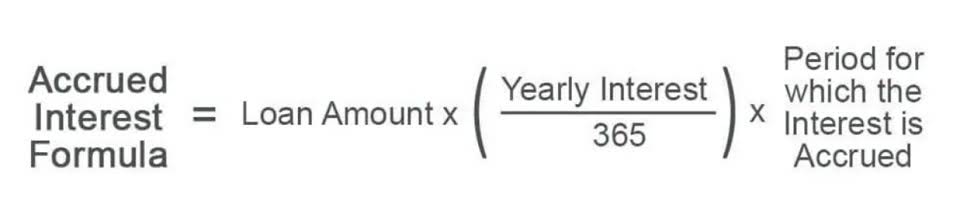It would involve calculating a known cost (like Labor cost) and then applying an overhead rate (which was predetermined) to this to project an unknown cost (which is the overhead amount). The formula for calculating Predetermined Overhead Rate is represented as follows. In these situations, a direct cost (labor) has been replaced by an overhead cost (e.g., depreciation on equipment). To account for these changes in technology and production, many organizations today have adopted an overhead allocation method known as activity-based costing (ABC). This chapter will explain the transition to ABC and provide a foundation in its mechanics. The allocation of overhead to the cost of the product is also recognized in a systematic and rational manner.
- The declining balance method involves using a constant rate of depreciation applied to the asset’s book value each year.
- In large ones, each production department computes its own rate to apply overhead cost.
- For example, if we choose the labor hours to be the basis then we will multiply the rate by the direct labor hours in each task during the manufacturing process.
- However, the problem with absorption/traditional costing is that we have to ignore individual absorption bases and absorb all overheads using a single level of activity.
- This activity base is often direct labor hours, direct labor costs, or machine hours.
- Manufacturing overhead is the sum of all the manufacturing costs except direct labor or direct materials costs.
Advantages of predetermined overhead rate formula
According to a survey 34% of the manufacturing businesses use a single plant wide overhead rate, 44% use multiple overhead rates and rest of the companies use activity based costing (ABC) system. You may also track the manufacturing overhead rate of your production process to determine the degree to which overhead costs increase the cost of manufacturing your products. The costs from the overhead budget are also used for calculating the cost of finished goods Restaurant Cash Flow Management inventory, which goes into the budgeted balance sheet. Additionally, this budget will allow you to calculate a predetermined manufacturing overhead rate, which you can then use to measure your production costs.

Calculating Manufacturing Overhead Cost for an Individual Job
Sales of each product have been strong, and the total gross profit for each product is shown in Figure 6.7. Using the Solo product as an example, 150,000 units are sold at a price of $20 per unit resulting in sales of $3,000,000. The cost of goods sold consists of direct materials of $3.50 per unit, direct labor of $10 when is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate computed? per unit, and manufacturing overhead of $5.00 per unit.

Overhead Rate Calculation: Accounting Explained
The predetermined rate is based on estimates before the accounting period begins and is held constant throughout the period. The overhead is applied to the product units at the rate of 2.50 for each labor hour used. Two companies, ABC company, and XYZ company are competing to get a massive order that will make them much recognized in the market. This project is going to be lucrative for both companies but after going over the terms and conditions of the bidding, it is stated that the bid would be based on the overhead rate. This means that since the project QuickBooks would involve more overheads, the company with the lower overhead rate shall be awarded the auction winner. Carefully minimizing overhead is crucial for small businesses to maintain profitability.
Deliver your projectson time and on budget
With $2.00 of overhead per direct hour, the Solo product is estimated to have $700,000 of overhead applied. When the $700,000 of overhead applied is divided by the estimated production of 140,000 units of the Solo product, the estimated overhead per product for the Solo product is $5.00 per unit. The computation of the overhead cost per unit for all of the products is shown in Figure 6.4. Overhead costs are then allocated to production according to the use of that activity, such as the number of machine setups needed. In contrast, the traditional allocation method commonly uses cost drivers, such as direct labor or machine hours, as the single activity. The production manager has told us that the manufacturing overhead will be $ 500,000 for the whole year and the company expected to spend 20,000 hours on direct labor.